27 December 2018 – The Warsaw Stock Exchange introduced dividend point indices: WIG20dvp, mWIG40dvp, sWIG80dvp. Dividend point indices (dvp) are calculated only on the basis of cash dividends paid by the constituents of the underlying index (WIG20, mWIG40 and sWIG80 respectively). Company’s dividend in calculation of dvp indices is taken into index calculation on “ex-dividend” date, it is on a session date on or after which a stock is traded without previously declared dividend. Due to the fact that dvp are calculated as the running total of ordinary dividends paid by the constituents of underlying index the value of the index is reset to zero once a year.
Please find below additional information explaining in detail index calculation methodology as well as publication mode for dividend point index having WIG20dvp as example. All the rules are also applicable to the remaining dvp indices to be offered by the Warsaw Stock Exchange : mWIG40dvp and sWIG80dvp.
Brochure
Methodology
Press release
WIG20dvp index >>
mWIG40dvp index >>
sWIG80dvp index >>
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does “dvp” stand for in the name of WIG20dvp?
WIG20dvp is presented in index points. Index points of a dividend index such as WIG20dvp are called dividend points, hence the abbreviation dvp.
2. How do I get information about dividends paid by WIG20 stocks by reading WIG20dvp?
To understand how, take the following example. Let’s say that WIG20 is not an index but a stock listed on GPW. Let’s assume that the price of such stock is PLN 2,000, equivalent to 2,000 WIG20 index points, at the beginning of the year. Now, if WIG20dvp is 40 points at the end of the year, then the virtual stock has paid dividends of PLN 40 during the year. An investment of PLN 2,000 has generated a dividend income of PLN 40. The return rate is 2% (PLN 40 / PLN 2,000). To simplify, this is how WIG20dvp works.
3. What dividends are reflected in WIG20dvp?
Only cash dividends as well as advance dividends. The index also includes conditional dividends but only if the trading day when the stock trades “without dividend” is later than the date when the issuer decides to pay the dividend (later than the day of fulfilment of the dividend condition).
4. How does WIG20dvp present incremental dividends?
WIG20dvp tracks dividends paid by WIG20 stocks during the year. WIG20dvp starts at 0 at the beginning of the year (no dividend paid) and goes up as more and more companies pay dividends. At each publication date, WIG20dvp reflects the current dividends as well as all dividends paid since the beginning of the year. This is why WIG20dvp can only go up and never goes down with the exception of the year’s end when the index is reset. The index is reset before the next annual index period begins.
5. How is WIG20dvp different from WIG20 and WIG20TR?
WIG20dvp is a dividend index based on dividend income earned on stocks. It tracks the investor’s income earned on dividends paid by stocks participating in WIG20. It represents the part of the investment which the investor keeps in the portfolio rather than reinvesting it after receiving a dividend.
WIG20 is a price index. It is calculated only based on prices of transactions in stocks participating in the index portfolio. It tracks changes in prices of the investor’s portfolio of WIG20 stocks in proportion to the portfolio composition. It does not include such income as dividends or subscription rights.
WIG20TR is a total return index. In contrast to WIG20, it tracks both transaction prices and income such as dividends and subscription rights. Importantly, the index methodology assumes that returns are reinvested in the stocks. The index reflects all dividends and subscription rights of WIG20TR stocks since the creation of the index.
The table below provides a comparison of WIG20dvp, WIG20, and WIG20TR. The table presents the data used to calculate the indices.
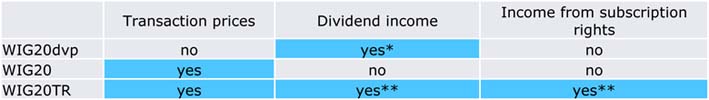 * Including dividend income earned during the year, which is not reinvested.
** Including all income since the creation of the index (not just income earned during the year), which are reinvested in the stock portfolio.
* Including dividend income earned during the year, which is not reinvested.
** Including all income since the creation of the index (not just income earned during the year), which are reinvested in the stock portfolio.
6. When are dividends first reflected by WIG20dvp? On the date of payment?
A dividend is included in WIG20dvp as of the trading day on which the stock is first traded “without dividend”. Note that a dividend is included in the index earlier than the payment date.
7. If a WIG20dvp stock pays a dividend and is later removed from WIG20, is the dividend removed from WIG20dvp?
If a stock is removed from WIG20 after it pays a dividend included in WIG20dvp, the dividend is not removed from the index. WIG20dvp always reflects all dividends paid by WIG20 stocks year to date, including stocks which have been removed from WIG20.
8. Why is WIG20dvp reset at the year’s end?
WIG20dvp presents dividends paid by WIG20 stocks during the current year rather than incremental dividends paid over the years. The index is reset at the end of the year and tracks dividends from scratch in the following year. The index is reset at the first trading session after the third Friday in December.
9. Why is WIG20dvp last calculated in the year before a reset on the third Friday in December (or the last trading day before the third Friday in December if there is no trading on the third Friday) rather than the day of the last trading session in the year?
The third Friday in December (or the last trading day before the third Friday in December if there is no trading on the third Friday) is not only the last day of calculation of WIG20dvp before the index is reset but also the expiry date of WIG20 futures and WIG20 options. This is no coincidence. WIG20dvp can serve as a useful source of information for investors trading in WIG20 futures and options because their valuation should factor in dividends paid by the stocks in the underlying index. This is why the WIG20dvp annual calculation period ends on the last day when derivatives expire during the year.
10. What if a WIG20 stock pays a dividend (the stock is first traded “without dividend”) on the trading day after the third Friday in December? Is the dividend included in WIG20dvp even though this is when the index is reset?
First of all, note how WIG20dvp is reset. WIG20dvp is reset at the trading session after the third Friday in December, which means that dividends paid before that date are no longer reflected in the index. The index starts a new annual calculation period on that date and tracks dividends paid by WIG20 stocks in the new period. If a dividend is paid on a trading day after the third Friday in December, it is reflected in WIG20dvp as a dividend paid in the new annual calculation period. In that case, the index is not equal to 0 when first published as it includes the dividend paid.
11. How frequently is WIG20dvp published?
WIG20dvp is published once per day at 11:00. All index values are published, including 0 which means that no dividend has yet been paid by WIG20 stocks.
12. If WIG20 includes prices of transactions of stocks in the portfolio while WIG20TR reflects dividend income, do I get WIG20dvp by subtracting WIG20TR from WIG20?
This is incorrect. Note that WIG20TR tracks all dividends paid by WIG20 stocks since the creation of the index while WIG20dvp only includes dividends paid during the year. Furthermore, WIG20TR assumes that dividends are reinvested while WIG20dvp does not. Importantly, WIG20TR includes income from subscription rights, as well.
13. Is WIG20dvp calculated in the same way as WIGdiv?
These are two different indices and their calculation methodologies are different, as well. WIG20dvp is a dividend index which only reflects cash dividends. The index presents “net” incremental dividends paid by WIG20 stocks during the year. WIGdiv is not a dividend index. It is a total return index tracking transaction prices as well as income from dividends and subscription rights. It is marked “div” because the index portfolio is comprised of stocks which regularly pay dividends.
14. How can I invest in WIG20dvp?
Similar to any exchange index, direct investment is not possible. However, you can invest in the index by means of a financial instrument for which the index is the underlying (i.e., the value of the financial instrument depends on the value of the index). At this time, WIG20dvp is not the underlying of any financial instrument.




