Predefined term index
The predefined term index will be calculated as an interest rate at the end of the term (in arrears) through compounding of interests resulting from the ON index (represented by the selected index) calculated by the Administrator for each working day of a given period preceding the date of determination and publication of the predefined term index.
The compounded rate calculation algorithm for a predefined period of XX
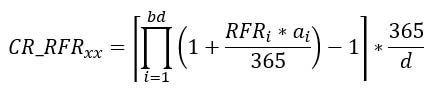
where:
CR_RFRxx – compounded interest rate1 based on the RFR index for the XX period (e.g. 1-month period), calculated with 5 decimal places2.
Rounding will take place at the end of the CR_RFR calculation (see below).
RFRi – value of the chosen RFR index for ON term for the i-th business day falling in the XX interest period, for which the calculation of CR is made; the value of RFR for the i-th business day is determined and published on the next business day.
ai – number of calendar days for which the RFRi is applied. For example, a rate determined for Monday is valid for one day - until Tuesday (if Tuesday is a business day), a rate determined for Friday is valid for 3 days – until Monday.
bd – number of working days in the XX interest period for which the calculation is made, including the first day of the period and excluding the last day of the period where XX assumes the value of 1M, 3M and 6M.
d – number of calendar days in the interest period XX for which the calculation is made, including the first day of the period and excluding the last day of the period.
Interest period determination rules
The last day of the interest period (end date) is always the day of calculating the compound interest rate – it has to be a business day.
The first day of the interest period (start date) is a business day falling on a day that precedes the calculation date by a certain number of months (1M, 3M or 6M). It is determined in accordance with the ‘modified preceding’ convention, described in accordance with the following rule:
If a potential start date resulting from a calendar shift of a given end date back by a certain number of months (i.e. a shift of the n-th day of a given month by 1 month gives the n-th day of the previous month) would fall on a non-working or a nonexistent day (e.g. 30th February), then the closest working day preceding the potential start date should be selected for the start date, unless it falls already in the previous month - in which case the next working day following the potential start date should be selected. If the potential start date is a business day, it should be selected for the start date.
Fixed-base index – Compound Index CI
Fixed-base index is considered to be an index expressed in index points. The Compound Index (CI) represents the value of an investment with a Starting Value of CI0 renewing on each CI Calculation Day (with interest capitalization) beginning from the Start Day, at a rate of return equal to the value of the RFR Index, where:
– Start Day – the day of the beginning of the calculation of the fixed-base index, which was set in the rules of the relevant index,
– Start Value (CI0) – the value of the fixed-base index on the Start Day, i.e. the number being part of its method, which has been set at 100,
– RFR index – one of the ON indices,
– Index Day – the day to which the given RFR index refers (the date of ON transactions, based on which the index is calculated),
– CI Calculation Day – the day of the fixed-base index3 on which this index is calculated, i.e. each business day starting from the Start Day (on each subsequent CI Calculation Day the value of the fixed-base index is calculated taking into account the last available value of the RFR index in accordance with its method).
The fixed-base index, i.e. the CI index, is calculated on the basis of the following formula:
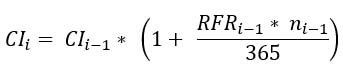
where:
CIi – value of the fixed-base index (expressed in index points) for the i CI Calculation Day, calculated on the i CI Calculation Day, published with 8 decimal places precision (in the calculation of CIi an unrounded value of CIi-1 is used),
RFRi-1 – value of the RFR Index4 for the Index Day of i-1, i.e. the business day preceding the Calculation Day i in accordance with the RFR index method),
ni-1 – number of calendar days between the i-1 CI Calculation Day and the i CI Calculation Day (e.g. when the i-1 CI Calculation Day is Friday and the i CI Calculation Day is Monday, then ni-1 = 3).
The use of the CI index for the calculation of interest rate value over a specific period is possible by applying the following formula, according to which the change in the CI index value between the x and y dates is calculated, according to the formula:
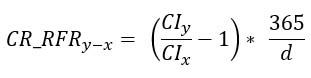
where:
x – date of the beginning of the interest period
y – date of the end of the interest period
CR_RFRy-x – compound interest rate for the period from date x to date y
CIx – value of the fixed-base index for the x CI Calculation Day
d – number of calendar days from date x to date y
Rounding and publication rules
For the avoidance of doubt, the rounding precision rules and rules of publication of indices have been defined. According to them:
(1) ON indices will be calculated and presented with 3 decimal places precision5
(2) indices for predefined terms will be calculated and published with 5 decimal places precision6
(3) the fixed-base index expressed in index points will be calculated with 8 decimal places precision with a base value of 100, with the start date of the index being the date set in the rules of the relevant index.
The Rules for the Method of Compound Indices in the event of undetermined value of Risk-Free Rate
Should Risk-Free Rate be undetermined for a given Business Day, the last determined RFR value for the RFR Index Date preceding the Business Day on which the RFR was undetermined shall be adopted to determine the RFR Compound Index for the RFR value for the Business Day on which the RFR was undetermined. In the example set out below RFR is undetermined for the Index Date 08.07.2025, which means, that RFR is undetermined and undistributed on a Business Day 09.07.2025, and consequently RFR Compound Index was undetermined and undistributed on the 09.07.2025 for that day. The following day, once the factors that prevented determination and distribution of RFR subside and thus the RFR as well as the RFR Compound Index can be determined and distributed on the 10.07.2025, the RFR Compound Index shall be determined assuming that in place of the undetermined and undistributed RFR value on the Business Day 09.07.2025 for the Index Date 08.07.2025, the last determined and published RFR value shall be used, namely the RFR value determined and distributed on the 08.07.2025 for the Index Date 07.07.2025. The presented example has been limited to chosen Index Dates and illustrates a scenario in which the RFR Compound Index is undetermined and undistributed for one Business Day, nonetheless such situation may occur repeatedly.
In order to determine the RFR Compound Index in the presented example for the 10.07.2025 (once the factors that prevented determination and distribution of RFR, for the Business Day 09.07.2025, subside), for the Business Day 09.07.2025, on which the RFR was undetermined and undistributed for the RFR Index Date 08.07.2025, shall be adopted the last determined and distributed RFR value for the Business Day 08.07.2025 (Index Date 07.07.2025):
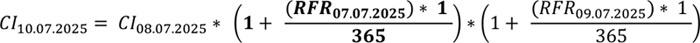
where:
CIdd.mm.yyyy – value of the RFR Compound Index as of the RFR Compound Index Date dd.mm.yyyy,
RFRdd.mm.yyyy – value of the RFR as of the Index Date dd.mm.yyyy.
Figure 1. RFR Compound Index
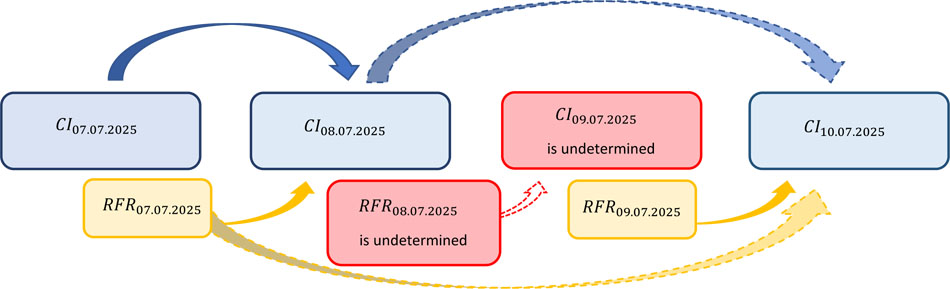
Figure 1. illustrates graphical representation of the Rules for the Method of RFR Compound Index, which when factors preventing determination and distribution of the RFR as well as RFR Compound Index subside, determine the rules of restoration of the RFR Compound Index determination process.
Should Risk-Free Rate be undetermined for a given Business Day within the RFR Compound Rate Reference Period (excluding the Reference Period end date), the last determined RFR value for the RFR Index Date preceding the Business Day on which the RFR was undetermined shall be adopted to determine the RFR Compound Rate for the RFR value for the Business Day on which the RFR was undetermined. In the example set out below RFR is undetermined for the Index Date 08.07.2025, which means, that RFR is undetermined and undistributed on a Business Day 09.07.2025, and consequently RFR 1M Compound Rate was undetermined and undistributed on the 09.07.2025 for that day (in this example RFR 1M Compound Rate is presented) . The following day, once the factors that prevented determination and distribution of RFR subside and thus the RFR as well as the RFR 1M Compound Rate can be determined and distributed on the 10.07.2025, the RFR 1M Compound Rate shall be determined assuming that in place of the undetermined and undistributed RFR value on the Business Day 09.07.2025 for the Index Date 08.07.2025, the last determined and published RFR value shall be used, namely the RFR value determined and distributed on the 08.07.2025 for the Index Date 07.07.2025. The presented example has been limited to chosen Index Dates and illustrates a scenario in which the RFR 1M Compound Rate is undetermined and undistributed for one Business Day, nonetheless such situation may occur repeatedly.
In order to determine the RFR 1M Compound Rate in the presented example for the 10.07.2026 (once the factors that prevented determination and distribution of RFR, for the Business Day 09.07.2025, subside), for the Business Day 09.07.2025, on which the RFR was undetermined and undistributed for the RFR Index Date 08.07.2025, shall be adopted the last determined and distributed RFR value for the Business Day 08.07.2025 (Index Date 07.07.2025):
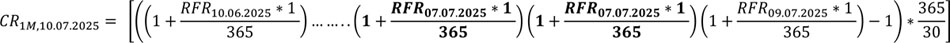
where:
CR1M,dd.mm.yyyy – the value of the RFR 1M Compound Rate as of the RFR 1M Compound Rate Index Date dd.mm.yyyy,
RFRdd.mm.yyyy – value of the RFR as of the Index Date dd.mm.yyyy.
Figure 2. RFR 1M Compound Rate
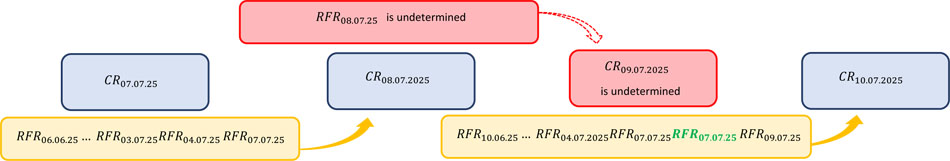
Figure 2. illustrates graphical representation of the Rules for the Method of RFR 1M Compound Rate, which when factors preventing determination and distribution of the RFR as well as RFR 1M Compound Rate subside, determine the rules of restoration of the RFR 1M Compound Rate determination process.
1 CR_RFR and RFR indices are interest rates, so, for example, CR_RFR may be equal to 5.12345%, which is equivalent to the number 0.0512345, RFR index may be equal to 5.123%, which is equivalent to the number 0.05123.
2 Rounding is applied to an interest rate expressed in %, so an example of an interest rate rounded to 5 decimal places is 5.12345%..
3 On the Administrator's website the day of the fixed-base index is the same day as the day of its publication and calculation.
4 RFR index is an interest rate, so, for example, RFR may be equal to 5.123%, which is equivalent to the number 0.05123.
5 Rounding is applied to an interest rate expressed in %, so an example of an interest rate rounded to 3 decimal places is 5.123%.
6 Rounding is applied to an interest rate expressed in %, so an example of an interest rate rounded to 5 decimal places is 5.12345%.



